Bacteria Imbalances in the gut are linked to Microbial Alterations in the lungs
Your Microbiome, Immunity, Cleaning Products and More
“A leaky barrier somewhere (e.g., in the gut) means a leaky barrier elsewhere (the lungs),” a mentor once told me long ago.
But back in 2006, we didn’t have a respiratory virus circulating, so I cached the thought away…
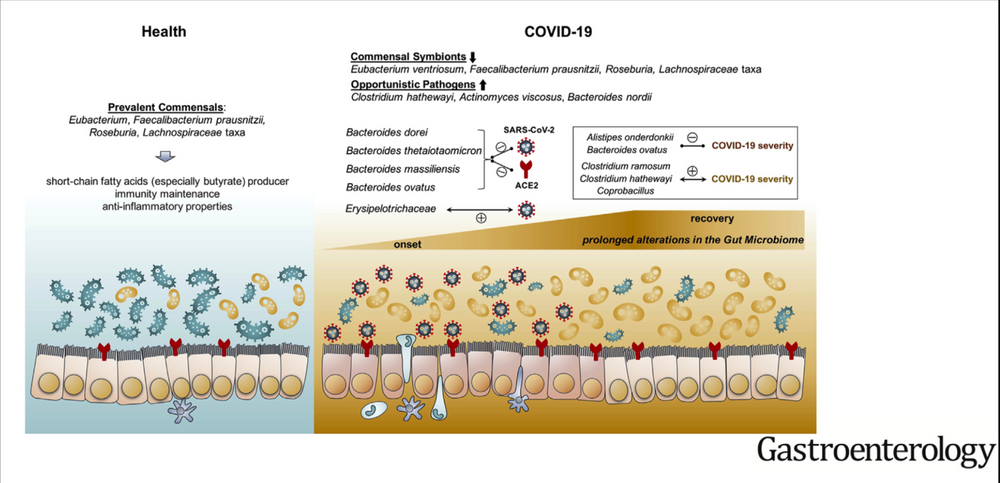
In the COVID-19 era, scientists are reporting that dysbiosis (bacterial imbalances in the gut) are linked to severe outcomes. (Aktas 2020)
Related Product: Probio Supreme High Potency Probiotic
Scientists say that dysbiosis in the gut are linked to imbalances in the lungs (respiratory microbiome) and increase the “leakiness” of the protective barriers of both tissues.
The implications of this gut-lung axis conversation have long-term implications from a food and environment perspective.
A few things we consider in the video above:
-Children raised in a highly sterile environment have higher levels of bacteria linked with obesity (Parks 2020)
-Food choices that may affect gut and possibly lung health
-Probiotics for those who have recently had antibiotics or take medicines that alter the microbiome
Related Product: Lean Gut Bugs, featuring Bifidobacterium animalis
References:
Aktas, B., & ASLIM, B. (2020). Gut-lung axis and dysbiosis in COVID-19. Turkish Journal of Biology, 44(3), 265–272. http://doi.org/10.3906/biy-2005-102
Angurana, S. K., & Bansal, A. (2020). Probiotics and COVID-19: Think about the link. British Journal of Nutrition, 1–26. http://doi.org/10.1017/S000711452000361X
Dhar, D., & Mohanty, A. (2020a). Gut microbiota and Covid-19- possible link and implications. Virus Research, 285, 198018–6. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198018
Parks, J., McCandless, L., Dharma, C., Brook, J., Turvey, S. E., Mandhane, P., et al. (2020). Association of use of cleaning products with respiratory health in a Canadian birth cohort. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 192(7), E154–E161. http://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.190819
Terruzzi, I., & Senesi, P. (2020). Does intestinal dysbiosis contribute to an aberrant inflammatory response to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in frail patients? Nutrition, 79-80, 110996–7. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2020.110996
Treatment of COVID-19 patients suspected with gut microbiota dysbiosis with washed microbiota transplantation: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. (2020). Treatment of COVID-19 patients suspected with gut microbiota dysbiosis with washed microbiota transplantation: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial, 1–20. http://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-56663/v1
xu, R., Liu, P., Zhang, T., Wu, Q., Zeng, M., Ma, Y., et al. (2020). Progressive worsening of the respiratory and gut microbiome in children during the first two months of COVID-19, 1–25. http://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.13.20152181
RECENT POSTS
CATEGORIES
- 5-MTHF
- Adrenals
- air quality
- Berberine
- caffeine
- Collagen
- Cortisol
- Creatine
- D-chiro-inositol
- Detoxification
- DHEA
- Electrolytes
- epigenetics
- Erythritol
- Exercise
- Fast Mimicking
- Fasting
- Fat Loss
- fires
- Glutathione
- Glycine
- gut bacteria
- Hormones
- IFOS
- Inositol
- INTERNATIONAL FISH OIL STANDARDS (IFOS) PROGRAM
- Iodine
- longevity
- magnesium
- Magnesium L Threonate
- Metabolic Health
- Microbiome
- minerals
- Monk Fruit
- Multivitamin
- myo-inositol
- N-acetyl cysteine
- NAC
- omega-3 index
- Post exercise
- Pre Workout
- Recipe
- Sleep
- Stevia
- vitamin
- Vitamin B12
- Weight Loss
- whey protein
- Women's Health
- Zinc
- Zinc Taste Test




